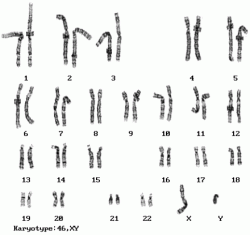
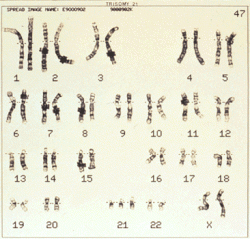
Dwarfism

Dwarfism has many different names, some of the names are ACH, Achondroplastic dwarfism, Chondrodystrophia fetalis, Chondrodystrophia syndrome, Congenital osteosclerosis, Dwarf/ Achondroplastic, and Osteosclerosis Congenital. The number of chromsomes affected are 4 and gene 3 has been affected. Dwarfism is mainly associated with a genetic disorder such a achondroplastia. About 80% of achondroplastia parents are average height. In dwarfism there are more than 200 medical conditions. A achondroplastic patient can be between the height of 2 feet 8 inches to 4 feet 8 inches. There are 2 types of dwarfism, disproportionate dwarfism and proportionate drwarfism. Treatments are unaffected, or in other words there is no cure to dwarfism. Surguries can be very harmful or dangerous or they can help with there disease. The X chromosome in dwarfism, in gene 3 is all messed up, so that affects the DNA to make the person smaller than they should be/ be a chondroplastic patient.
By: Cianna Chevalier
By: Cianna Chevalier
Coffin-Lowry Syndrome

Coffin-Lowry syndrome is one of the many mental retardation syndromes caused by abnormalities of the genes on the X chromosome. Coffin-Lowry syndrome (CLS) is also known as the Mental Retardation with Osteocartilaginous Abnormalities. CLS is an inherited gene mutation that affects a person mentally and physically. Some physical symptoms are under-developed upper jaw bone, abnormally thick and prominent eyebrows, downslanting eyelid folds, widely spaced eyes, and large ears. Types of treatments are physical therapy and speech therapy, but there is not cure. The prognosis is unpredictable. The gene for Coffin-Lowry syndrome, RSK2, is located on the short arm of the X chromosome. People with CLS have a much shorter life-span than average, passing on in their 30's. Luckly, Coffin-Lowry syndrome isn't a popular syndrome, affecting around only 1 in 40,000 to 50,000 people.
By: Jessica Ros
By: Jessica Ros
bibliography
"Coffin-Lowry syndrome - Genetics Home Reference." Genetics Home Reference - Your guide to understanding genetic conditions. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2009. <http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition=coffinlowrysyndrome>.
"Coffin-Lowry syndrome Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatments and Causes - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/c/coffin_lowry_syndrome/intro.htm>.
"Dwarfism Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatments and Causes - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/d/dwarfism/intro.htm>.
"Dwarfism: Treatments and drugs - MayoClinic.com." Mayo Clinic medical information and tools for healthy living - MayoClinic.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/dwarfism/DS01012/DSECTION=treatments-and-drugs>.
"Symptoms of Coffin-Lowry syndrome - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/c/coffin_lowry_syndrome/symptoms.htm>.
"dwarfism (medical disorder) -- Britannica Online Encyclopedia." Encyclopedia - Britannica Online Encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/174900/dwarfism>.
"Coffin-Lowry syndrome Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatments and Causes - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/c/coffin_lowry_syndrome/intro.htm>.
"Dwarfism Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatments and Causes - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/d/dwarfism/intro.htm>.
"Dwarfism: Treatments and drugs - MayoClinic.com." Mayo Clinic medical information and tools for healthy living - MayoClinic.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/dwarfism/DS01012/DSECTION=treatments-and-drugs>.
"Symptoms of Coffin-Lowry syndrome - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/c/coffin_lowry_syndrome/symptoms.htm>.
"dwarfism (medical disorder) -- Britannica Online Encyclopedia." Encyclopedia - Britannica Online Encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/174900/dwarfism>.